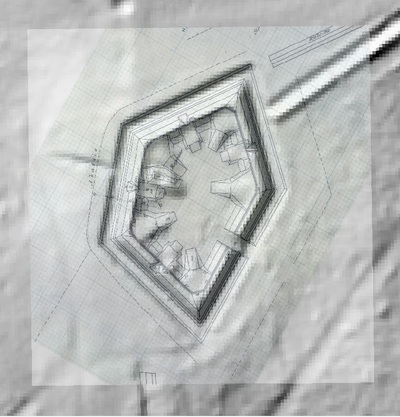
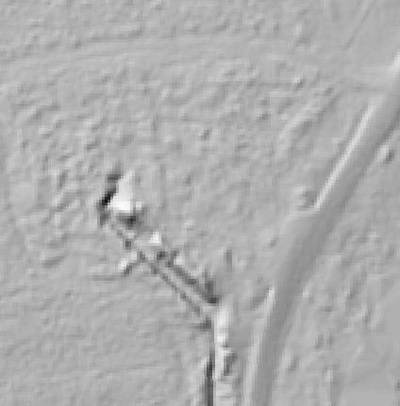
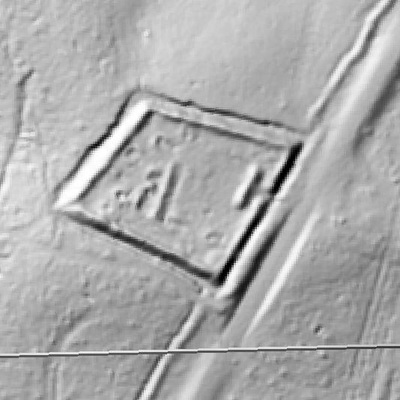
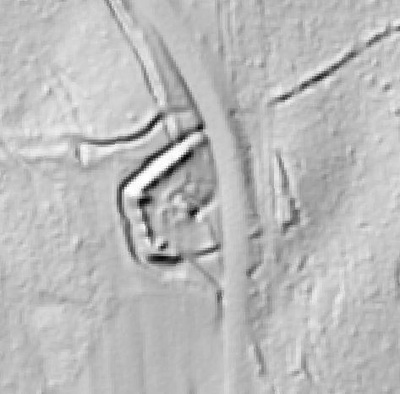
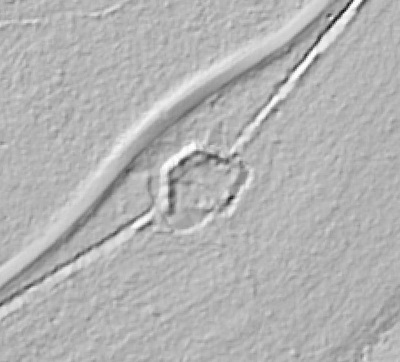
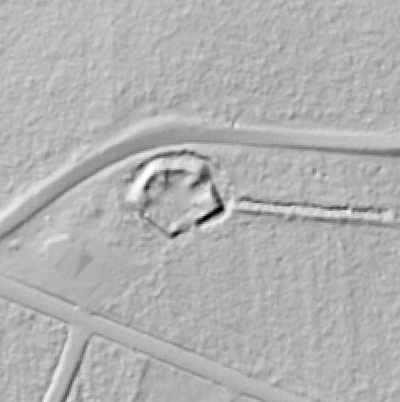
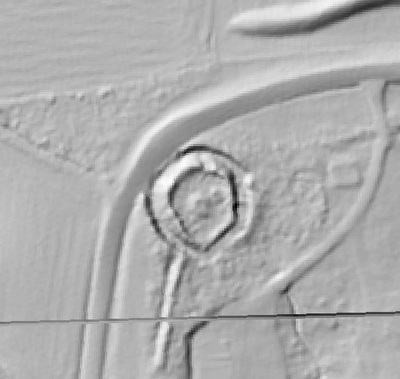
LIDAR, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing method that uses light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure ranges (variable distances) to the Earth. These light pulses—combined with other data recorded by the airborne system— generate precise, three-dimensional information about the shape of the Earth and its surface characteristics.
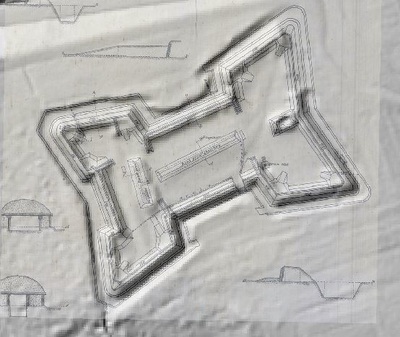
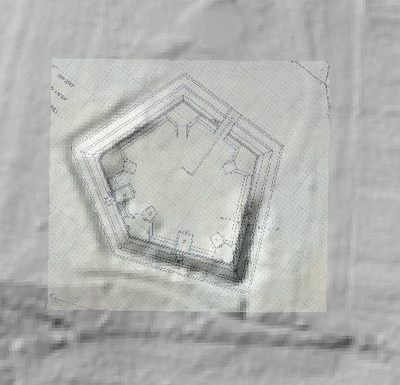
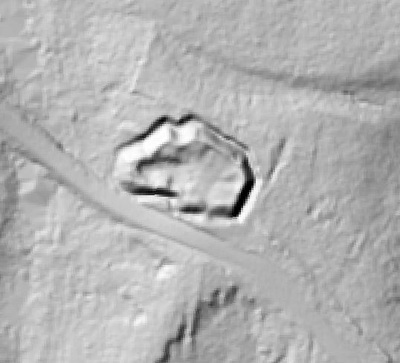
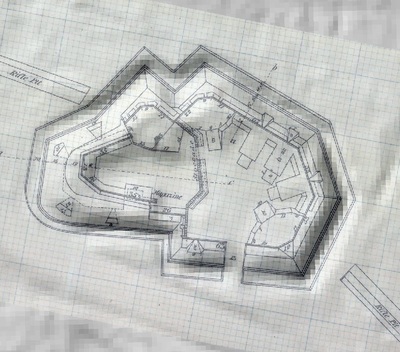
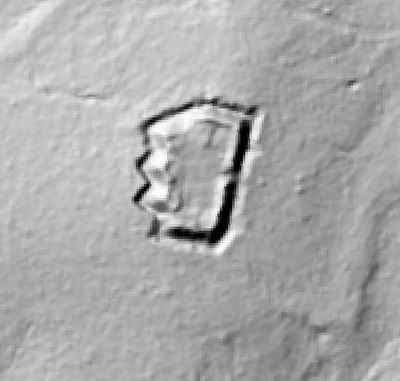
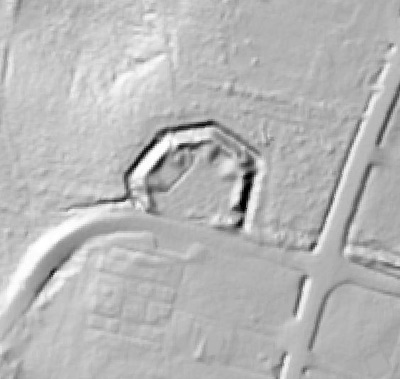
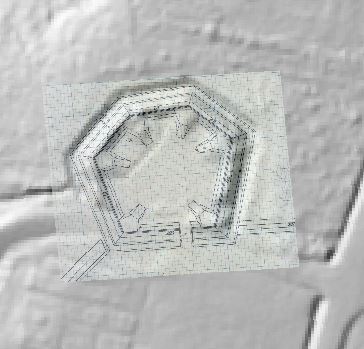
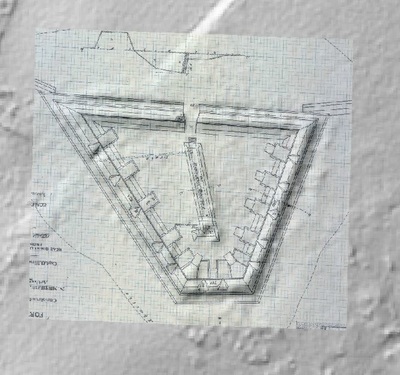
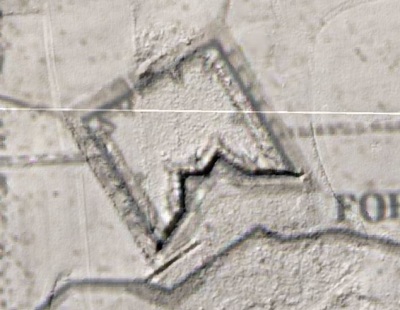
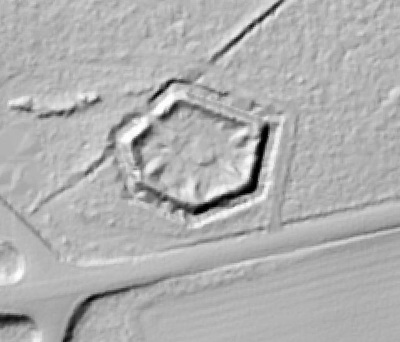
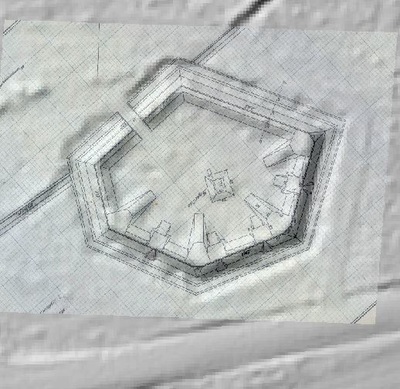
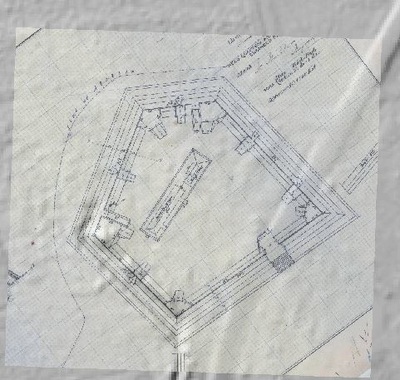
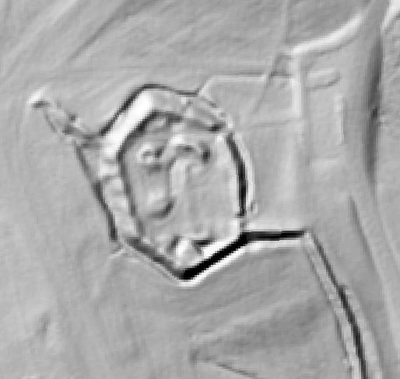
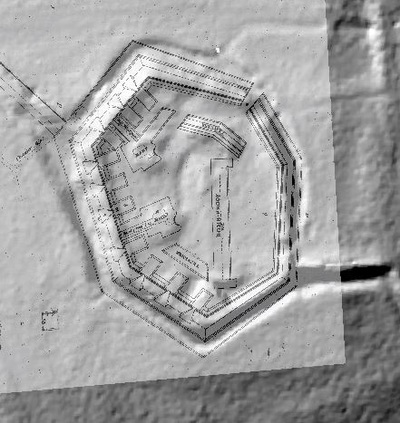
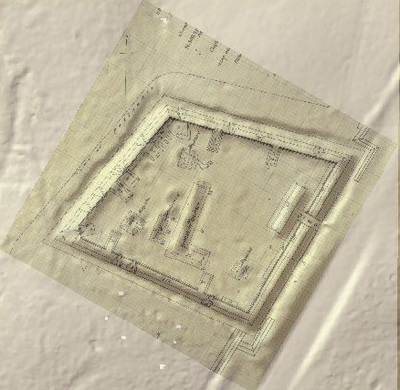
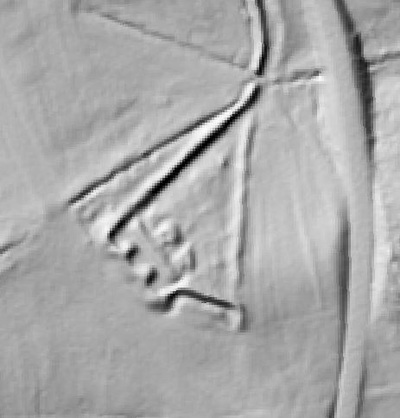
In 2014, Fort Lee shared digital elevation data derived from a LIDAR flyover with Petersburg National Battlefield. LIDAR has the ability to peer beneath forest cover to see minute changes in topography and to throw surviving earthworks in clear relief. The resolution of these images is about 1-meter. The Petersburg Project has seized upon the godsend of LIDAR to locate and document surviving fortifications within and adjacent to the national park. Below are illustrations of the interpretive power of this new technology.